Thumb arthritis
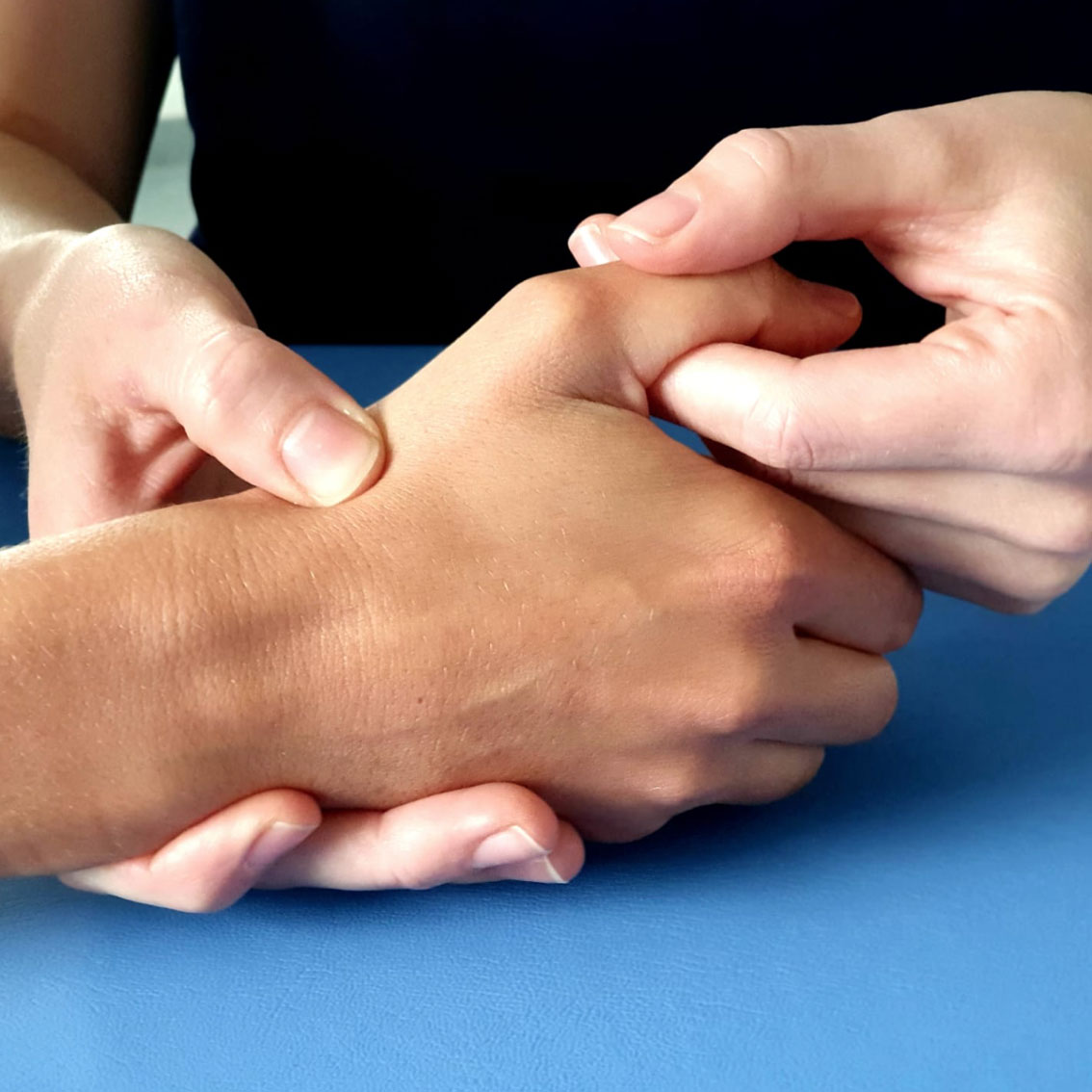
What is the thumb arthritis?
Thumb arthritis means wear of cartilage between the trapezium and the base of the first metacarpal.
This joint is subject to significant stress through everyday use (for example grasping, pinching, straining) which results in progressive destruction of cartilage. Over time, the cartilage becomes thinner, leading to grinding between two bones.
In advanced stages, bony spurs (osteophytes) may form in the joint, causing the metacarpal to slide out of the joint (thumb deformity).
What are the symptoms of thumb arthritis?
- Swelling and tenderness at the base of the thumb
- Loss of strength when gripping or pinching with the thumb
- Stiffness and progressive zig-zag “Z” deformity of the thumb
What are the causes and risk factors?
Thumb arthritis occurs after age 40 and is more common in women. The exact cause is unknown, but rather it is a combination of several factors :
How is the thumb arthritis diagnosed?
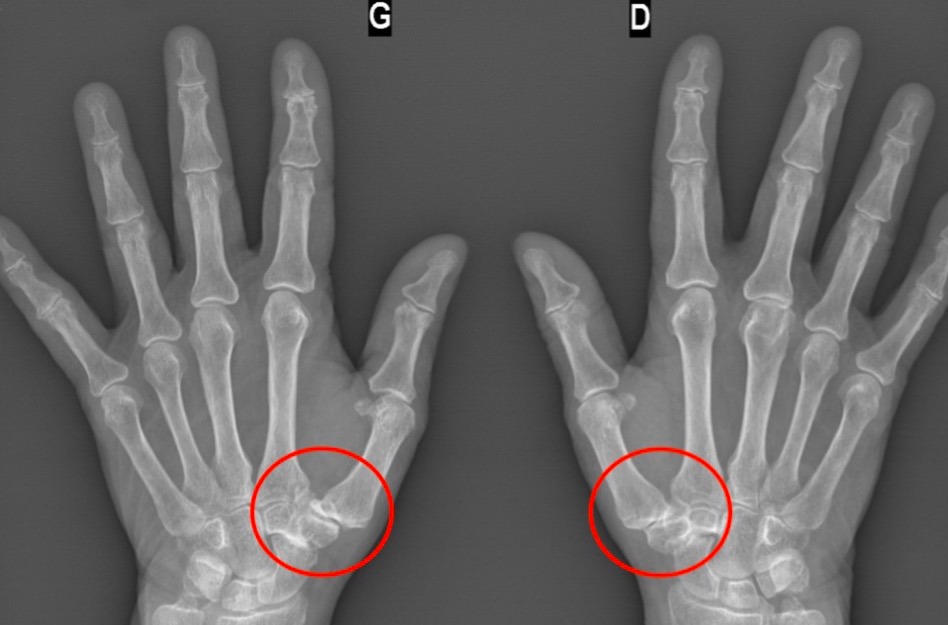
Your hand surgeon can diagnose the thumb arthritis by physical examination. X-rays are performed to determine the radiological stage of osteoarthritis, which is important when deciding on surgical treatment.
In these X-rays, we can see the 4 radiological stages, from the lightest on the left, to the complete destruction of the joint on the right.

How is thumb arthritis treated ?
- Resting, anti-inflammatory and icing the joint
- Bracing to limit the movement of the thumb (rest)
- Steroid injections into the basal joint (or hyaluronic acid / platelet concentrates)
- Exercises and ergonomic adjustments
- Occupational therapy
When should I have surgery?
If the pain is persistent and does not improve following medical treatment of at least six months, surgery should be considered. The type of surgery depends on the age of the patient, the type of manual activity and the radiological stage of osteoarthritis.
In beginner forms, it is possible to cut a strip of a tendon at the base of the thumb, in order to reduce pain, without compromising another future surgery.
Trapeziectomy consists of removing the trapezium, most often also stabilizing the joint using a tendon at the base of thumb.
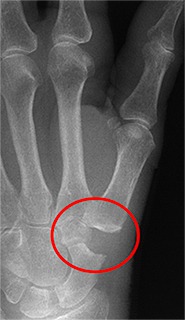
The damaged joint can be replaced by a carpometacarpal prosthesis (into trapezium and metacarpal bones). The prosthesis is made of titanium, with a dual mobility concept.

Trapeziectomy and prosthesis are very effective treatments to eliminate pain and allow a good recovery of thumb mobility in 3 to 6 months. The pinch strength (thumb - index) remains almost always reduced after surgery.
When to consult a specialist?
When pain begins to interfere with daily activities, a visit to the hand surgeon may be helpful.
Testimonial
"Dear Doctor
For the first time in a long time, I played golf without any pain or apprehension! I started again today and everything went very well.
I sincerely thank you for everything you have done because the result is beyond my expectations."