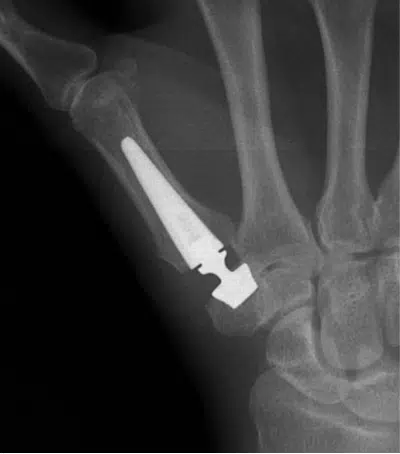
Thumb arthroplasty, or rhizarthrosis surgery, is a hand surgery procedure indicated when the pain associated with rhizarthrosis becomes too severe and can no longer be relieved by medical treatment. Rhizarthrosis is located at the base of the thumb, between the first metacarpal bone and the trapezium. It is caused by wear and tear of the articular cartilage, leading to pain and progressive deformation of the thumb, and lack of strength when holding an object or opening a bottle, for example. Arthritis of the thumb is very common, especially around the age of 50, and affects more women than men.
Rhizarthrosis surgery aims to reduce pain and restore thumb function, thus improving patients’ quality of life.
There are 2 main techniques: prosthetic arthroplasty, which replaces the damaged joint with a prosthesis, and trapezectomy, which removes the trapezium and stabilizes the thumb with a tendon.
In very early forms, it is possible to cut a strip of tendon at the base of the thumb, to reduce pain without compromising future surgery.