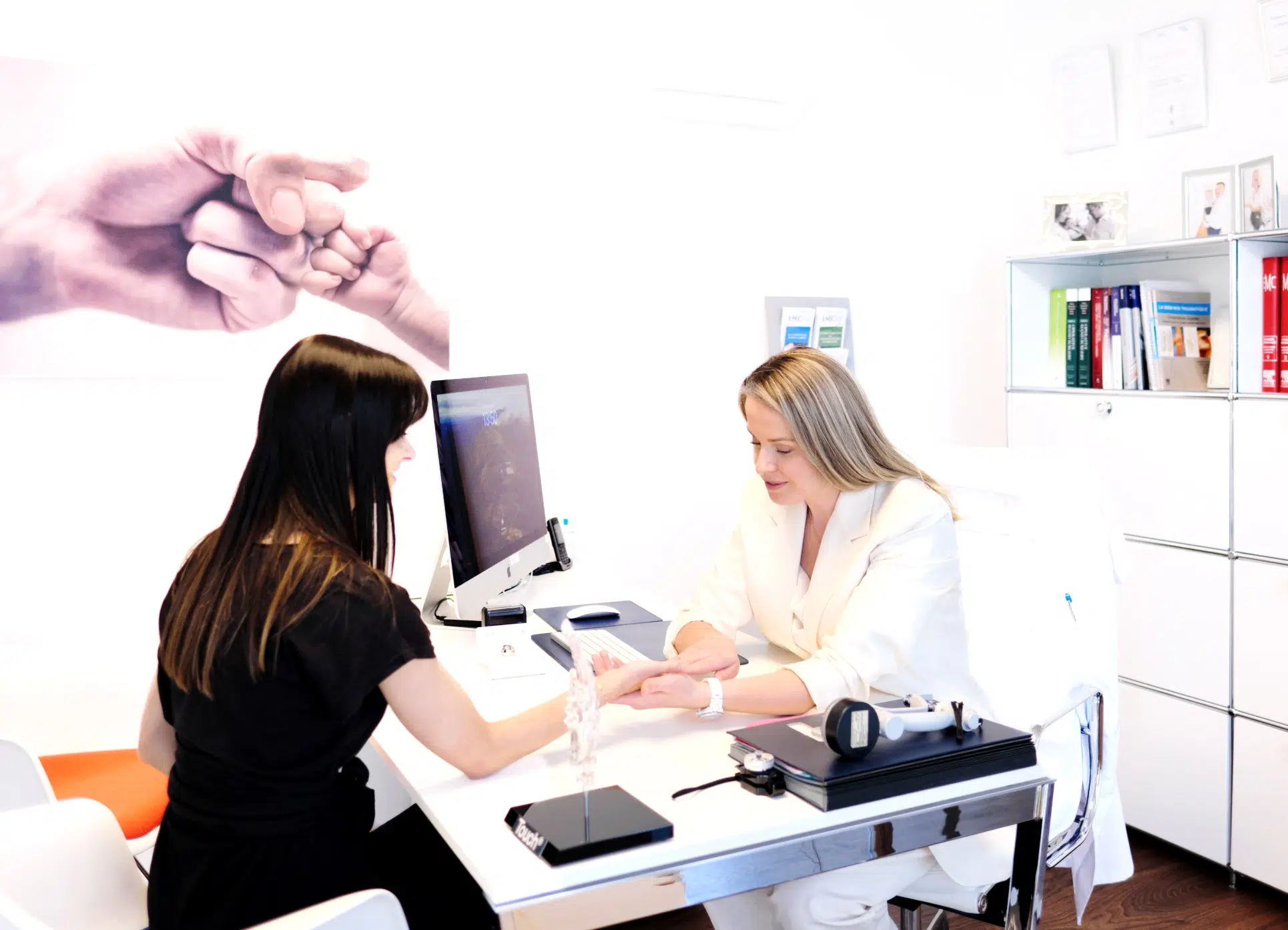
The Leman Hand Clinic offers comprehensive care for a wide range of hand and wrist pathologies. Our treatments include conservative options such as splints, occupational therapy and infiltrations, as well as surgical interventions aimed at relieving pain, restoring function and improving our patients’ quality of life.
Thumb arthritis
Thumb arthritis is a form of osteoarthritis affecting the base of the thumb, causing pain and stiffness. It results from wear of the cartilage of the trapeziometacarpal joint. Treatments may include splints and corticosteroid infiltration. When these options are not sufficient, surgical intervention, such as thumb prosthesis, may be considered to relieve pain and improve mobility.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by compression of the median nerve in the wrist. It manifests as numbness, tingling and pain in the hand and fingers. Non-surgical treatment includes a night-rest splint, occupational therapy and cortisone infiltrations. Definitive treatment involves decompression of the nerve at the wrist, providing rapid relief of symptoms in most cases.
Trigger finger
Trigger finger is characterized by the locking of a finger in the flexed position, followed by a “snap” when the finger is straightened. The condition is caused by inflammation of the flexor tendons at the entrance to the digital canal. Cortisone injections may suffice to eliminate the pain and blocking of the finger, with a recurrence rate of 50%. In the event of failure or recurrence of blockages, surgery can free the trapped tendons at the base of the finger, providing an immediate and lasting solution.
Dupuytren’s disease
Dupuytren’s disease causes thickening and retraction of the tissue under the skin of the palm, leading to progressive inward flexion of the fingers, with the inability to extend the fingers. There is no medical treatment for Dupuytren’s. When contractures are severe and the patient can no longer lay his or her hand flat, an operation can be performed to remove the indurated tissue and straighten the fingers.
Wrist fracture
Fractures of the wrist, in particular fractures of the distal radius, are common and often result from falls on the outstretched hand. They require specialized treatment by a hand surgeon, to ensure optimal recovery of mobility and avoid the risk of osteoarthritis. In the case of a stable, slightly displaced fracture, immobilization in a cast is recommended. In the case of complex or displaced fractures, surgery with internal plate fixation is required to re-establish bone alignment and allow the fracture to consolidate in an anatomical position. Treatment by a specialist hand and wrist surgeon offers the best chance of recovering wrist mobility without sequelae.
Osteoarthritis of the wrist
Osteoarthritis of the wrist is a progressive wearing away of the cartilage in the wrist joints, leading to pain, stiffness and loss of function. Treatment options include splints, occupational therapy and joint infiltration. When osteoarthritis is advanced and disabling, surgical options such as wrist prosthesis, partial arthrodesis or first-row resection of the carpal bones may be considered.
Ulnar nerve compression at the elbow
Ulnar nerve compression at the elbow, also known as cubital tunnel syndrome, causes pain and numbness in the little and ring fingers. Conservative treatments include ergonomic changes, night splints and occupational therapy follow-up. If symptoms persist, surgical ulnar nerve release or transposition may be performed to relieve nerve compression.
Digital mucous cyst
A finger mucous cyst is a small swelling filled with viscous fluid that forms near the finger joints, most often around the nail, sometimes causing nail deformity when the cyst presses on the nail matrix. Non-surgical treatment options include punctures and steroid injections. In the event of recurrence or significant discomfort, surgical excision of the cyst may be necessary, combined with a local flap or skin graft. The main risk is recurrence, as long as the joint remains mobile.